Primary sources triangle shirtwaist factory fire – Primary sources offer invaluable insights into the tragic events of the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire, providing firsthand accounts that illuminate the working conditions, safety hazards, and aftermath of this devastating industrial disaster.
These primary sources serve as essential tools for historians and researchers, offering a direct connection to the experiences of those who lived through this pivotal moment in American labor history.
Historical Context of the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire: Primary Sources Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire
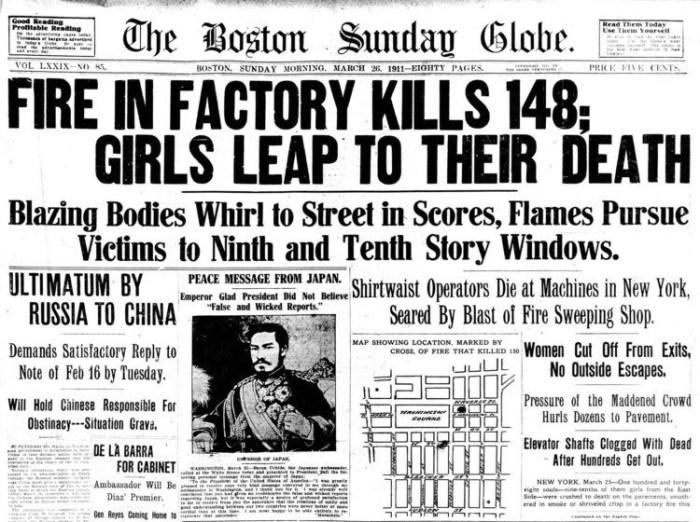
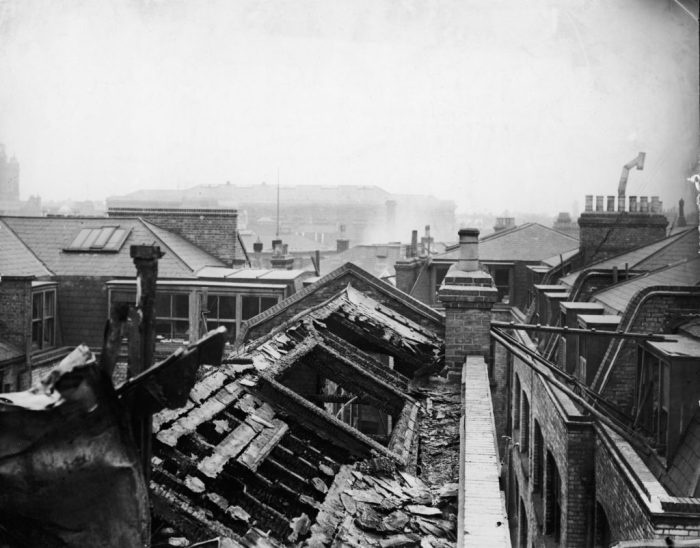
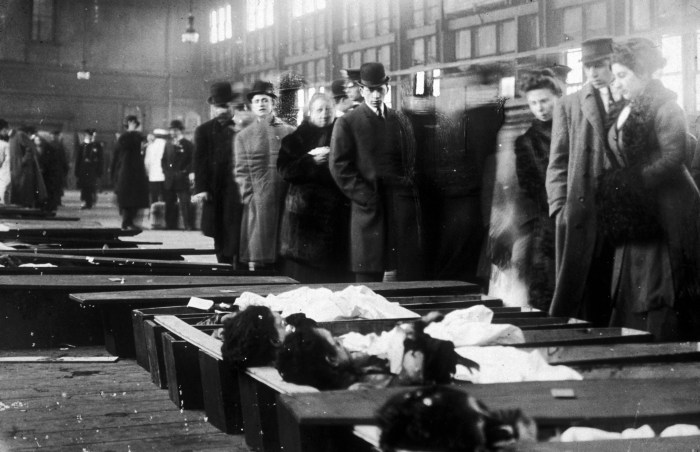
The Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire, a tragic event that occurred on March 25, 1911, in New York City, resulted in the deaths of 146 workers, predominantly young immigrant women. This incident marked a turning point in American labor history and highlighted the urgent need for workplace safety regulations.
The factory, located in the Asch Building in Manhattan, housed several garment workshops employing over 500 workers. The building lacked adequate fire safety measures, including fire escapes, sprinklers, and clear evacuation routes. Overcrowding and unsanitary conditions further exacerbated the risk of accidents.
The fire originated on the eighth floor of the building and quickly spread throughout the factory due to the presence of flammable materials and the lack of proper fireproofing. Many workers were trapped inside as the exits were either blocked or insufficient.
The tragedy shocked the nation and led to widespread outrage over the appalling working conditions and safety hazards faced by factory workers. It also prompted a wave of labor activism and the enactment of new laws to improve workplace safety and protect workers’ rights.
Causes and Contributing Factors, Primary sources triangle shirtwaist factory fire
The Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire was caused by a combination of factors, including:
- Inadequate Fire Safety Measures:The building lacked fire escapes, sprinklers, and proper evacuation routes, contributing to the rapid spread of the fire and the high number of casualties.
- Flammable Materials:The factory stored large amounts of flammable materials, such as fabric scraps and sewing machines, which fueled the fire’s intensity.
- Overcrowding:The factory was overcrowded with workers, making it difficult for them to evacuate quickly.
- Lack of Fire Drills and Safety Training:The workers had not received adequate fire safety training or conducted fire drills, which hindered their ability to respond effectively to the emergency.
- Locked Doors:Some exits were locked to prevent workers from taking unauthorized breaks, further obstructing their escape.
- Management Negligence:The factory management ignored safety concerns and failed to take appropriate measures to prevent a fire or ensure the safety of their workers.
Aftermath and Legacy
The Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire had a profound impact on American society and labor history:
- Public Outrage and Labor Activism:The tragedy sparked widespread outrage and led to increased public awareness of the dangerous working conditions faced by factory workers. It also galvanized labor activists to demand improved safety regulations and workers’ rights.
- New Labor Laws and Safety Regulations:In the wake of the fire, several new laws were enacted to improve workplace safety, including the Factory Investigating Commission, which investigated factory conditions and recommended safety improvements.
- Improved Building Codes:The fire also led to stricter building codes, requiring fire escapes, sprinklers, and other safety features in factories and other workplaces.
- Legacy of Labor Rights:The Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire is remembered as a symbol of the struggle for workers’ rights and the importance of workplace safety. It continues to inspire efforts to protect the safety and well-being of workers.
Question Bank
What were the main causes of the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire?
The fire was primarily caused by a combination of factors, including unsafe working conditions, inadequate fire safety measures, and management negligence.
What was the impact of the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire on labor laws?
The fire led to significant changes in labor laws, including the establishment of minimum wage laws, maximum hour laws, and improved safety regulations for factories.
How do primary sources contribute to our understanding of the Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire?
Primary sources, such as eyewitness accounts, photographs, and official reports, provide firsthand insights into the events of the fire, the experiences of the victims, and the subsequent investigations.