Bioflix activity membrane transport exocytosis and endocytosis – Bioflix Activity: Membrane Transport, Exocytosis, and Endocytosis offers an engaging exploration into the fundamental processes that govern the movement of molecules across cell membranes. These processes are essential for a wide range of cellular functions, from nutrient uptake to waste removal.
This activity provides an in-depth look at membrane transport, exocytosis, and endocytosis, equipping learners with a comprehensive understanding of these vital biological mechanisms.
Membrane Transport: Bioflix Activity Membrane Transport Exocytosis And Endocytosis
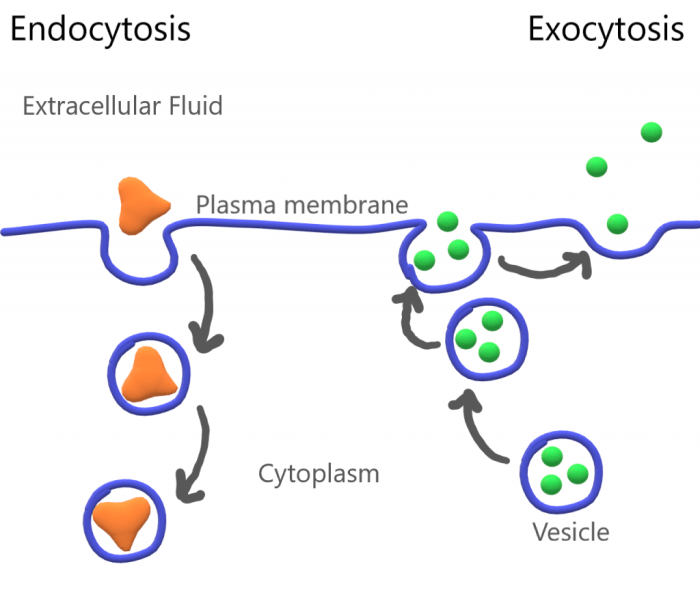
Membrane transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane. It is essential for the cell to maintain homeostasis, communicate with other cells, and obtain nutrients. There are two main types of membrane transport: passive and active.
Passive Transport
- Does not require energy.
- Molecules move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
- Examples: diffusion, osmosis
Active Transport
- Requires energy (ATP).
- Molecules move against their concentration gradient.
- Examples: sodium-potassium pump, calcium pump
Exocytosis
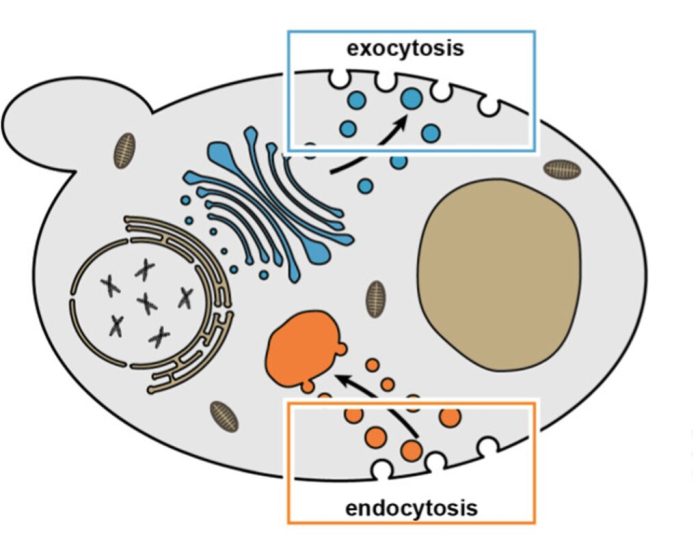
Exocytosis is the process by which cells release molecules outside the cell. It is used to secrete hormones, neurotransmitters, and other substances.
Steps Involved in Exocytosis
- The molecule to be secreted is packaged into a vesicle.
- The vesicle moves to the cell membrane.
- The vesicle fuses with the cell membrane.
- The molecule is released outside the cell.
Examples of Exocytosis
- Release of neurotransmitters at the synapse
- Secretion of hormones from endocrine glands
- Release of digestive enzymes from the pancreas
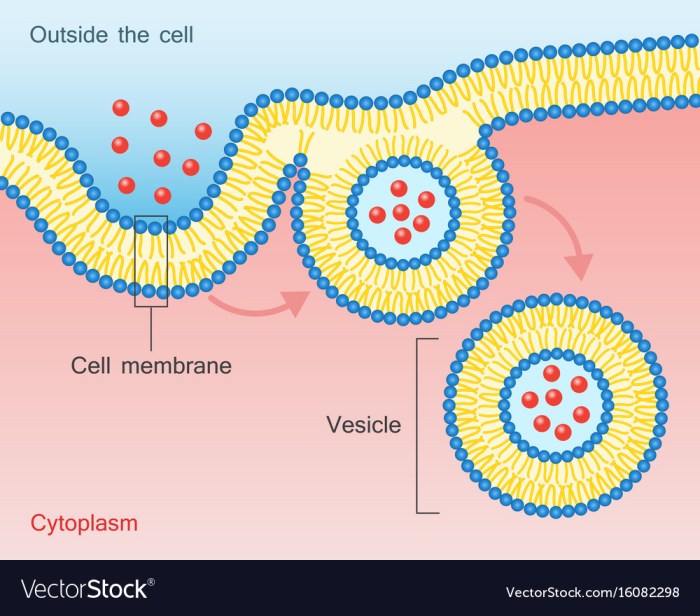
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is the process by which cells take in molecules from outside the cell. It is used to take in nutrients, hormones, and other substances.
Types of Endocytosis
- Phagocytosis:The cell engulfs a large particle.
- Pinocytosis:The cell takes in a small droplet of fluid.
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis:The cell takes in a molecule that binds to a specific receptor on the cell membrane.
Examples of Endocytosis, Bioflix activity membrane transport exocytosis and endocytosis
- Phagocytosis of bacteria by white blood cells
- Pinocytosis of nutrients by cells in the small intestine
- Receptor-mediated endocytosis of hormones by target cells
Comparison of Exocytosis and Endocytosis
| Feature | Exocytosis | Endocytosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Release of molecules outside the cell | Taking in of molecules from outside the cell |
| Energy requirement | Yes | No (for phagocytosis and pinocytosis); Yes (for receptor-mediated endocytosis) |
| Examples | Release of neurotransmitters, secretion of hormones | Phagocytosis of bacteria, pinocytosis of nutrients |
Biological Significance of Exocytosis and Endocytosis
Exocytosis and endocytosis are essential for a variety of cellular processes. Exocytosis allows cells to secrete hormones, neurotransmitters, and other molecules that are used to communicate with other cells. Endocytosis allows cells to take in nutrients, hormones, and other molecules that are used for metabolism and other cellular processes.
FAQ Insights
What is the difference between exocytosis and endocytosis?
Exocytosis is the process by which cells release molecules outside the cell, while endocytosis is the process by which cells take in molecules from outside the cell.
What are the different types of membrane transport?
There are two main types of membrane transport: passive transport and active transport. Passive transport does not require energy, while active transport requires energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient.
What are some examples of membrane transport in biological systems?
Membrane transport is essential for a wide range of cellular functions, including nutrient uptake, waste removal, and cell signaling.