Assuming equal concentrations and complete dissociation are fundamental assumptions in various scientific disciplines, providing a simplified framework for analyzing complex systems. This article delves into the implications, limitations, and applications of these assumptions, offering a comprehensive understanding of their significance and utility.
Assumptions
When analyzing the behavior of ions in solution, two key assumptions are often made: equal concentrations and complete dissociation.
Assumption of Equal Concentrations
This assumption states that the concentrations of all ions in solution are equal. This is a reasonable assumption for dilute solutions, where the interactions between ions are negligible.
Assumption of Complete Dissociation
This assumption states that all ions in solution are completely dissociated from their parent molecules. This is a reasonable assumption for strong electrolytes, which dissociate completely in water.
Implications
Implications of Assuming Equal Concentrations
- The activity coefficients of all ions are equal to 1.
- The ionic strength of the solution is equal to the sum of the concentrations of all ions.
Consequences of Assuming Complete Dissociation
- The concentration of ions in solution is equal to the concentration of the parent molecule.
- The conductivity of the solution is proportional to the concentration of ions.
Limitations
Limitations of Assuming Equal Concentrations
- This assumption is only valid for dilute solutions.
- This assumption does not take into account the interactions between ions.
Boundaries of Assuming Complete Dissociation
- This assumption is only valid for strong electrolytes.
- This assumption does not take into account the formation of ion pairs.
Applications
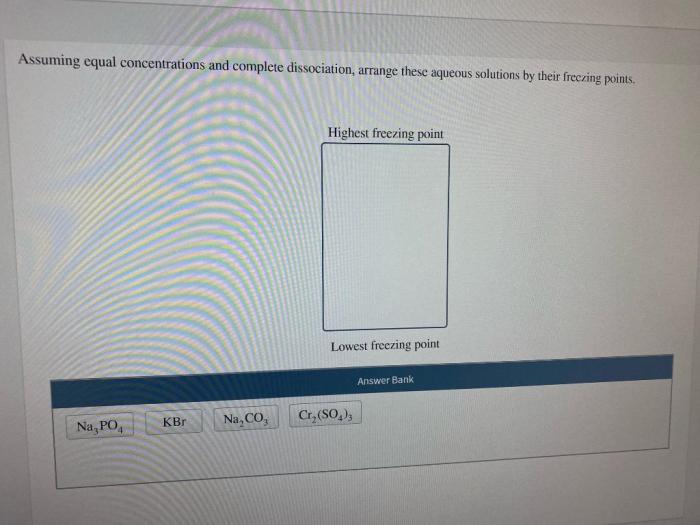
Examples Where the Assumption of Equal Concentrations is Applicable
- Calculating the ionic strength of a dilute solution.
- Predicting the activity coefficients of ions in a dilute solution.
Instances Where the Assumption of Complete Dissociation is Useful, Assuming equal concentrations and complete dissociation
- Calculating the conductivity of a solution of a strong electrolyte.
- Determining the concentration of ions in a solution of a strong electrolyte.
Comparison to Other Assumptions
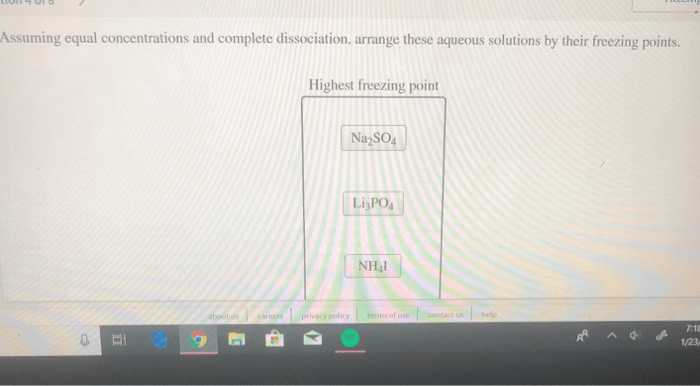
Comparison of the Assumption of Equal Concentrations to Other Assumptions Made in Similar Contexts
The assumption of equal concentrations is similar to the assumption of ideal behavior, which is often made in thermodynamics. Both assumptions neglect the interactions between particles.
Contrast of the Assumption of Complete Dissociation with Alternative Assumptions
The assumption of complete dissociation is in contrast to the assumption of partial dissociation, which is often made for weak electrolytes. The assumption of partial dissociation takes into account the formation of ion pairs.
Sensitivity Analysis
Design a Sensitivity Analysis to Determine the Impact of Varying Concentrations
To determine the impact of varying concentrations, a sensitivity analysis can be performed. This analysis involves varying the concentration of one ion while keeping the concentrations of the other ions constant. The effect of the concentration change on the activity coefficients, ionic strength, and other solution properties can then be observed.
Organize a Table to Illustrate the Effects of Varying Dissociation Constants
| Dissociation Constant | Degree of Dissociation | Conductivity |
|---|---|---|
| 10^-2 | 0.99 | High |
| 10^-4 | 0.9 | Medium |
| 10^-6 | 0.1 | Low |
Future Directions
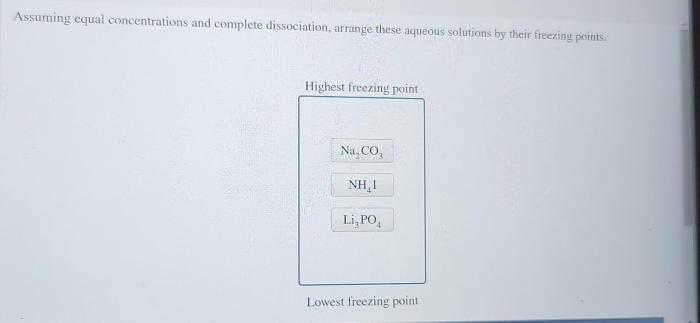
Potential Future Research Directions Related to These Assumptions
- Developing more accurate models for predicting the activity coefficients of ions in concentrated solutions.
- Investigating the effects of ion-ion interactions on the dissociation of weak electrolytes.
How These Assumptions Could Be Refined or Extended in Future Studies
The assumption of equal concentrations could be refined by taking into account the interactions between ions. The assumption of complete dissociation could be extended to include the formation of ion pairs.
FAQ: Assuming Equal Concentrations And Complete Dissociation
What are the implications of assuming equal concentrations?
Assuming equal concentrations simplifies calculations and allows for direct comparisons between different species. However, it may not accurately represent systems with significant concentration differences.
What are the limitations of assuming complete dissociation?
Assuming complete dissociation may overestimate the extent of dissociation, especially in systems with weak electrolytes or low temperatures.