Using latitude and longitude worksheet – Delve into the captivating world of latitude and longitude with our comprehensive worksheet guide. This engaging resource unravels the intricacies of these coordinates, empowering you to navigate the globe with precision and unlock a wealth of real-world applications.
As we embark on this journey, you’ll gain a profound understanding of latitude and longitude, their significance in navigation and mapping, and the art of interpreting their coordinates. Prepare to immerse yourself in a world of geographical exploration and discovery.
Definition and Importance: Using Latitude And Longitude Worksheet
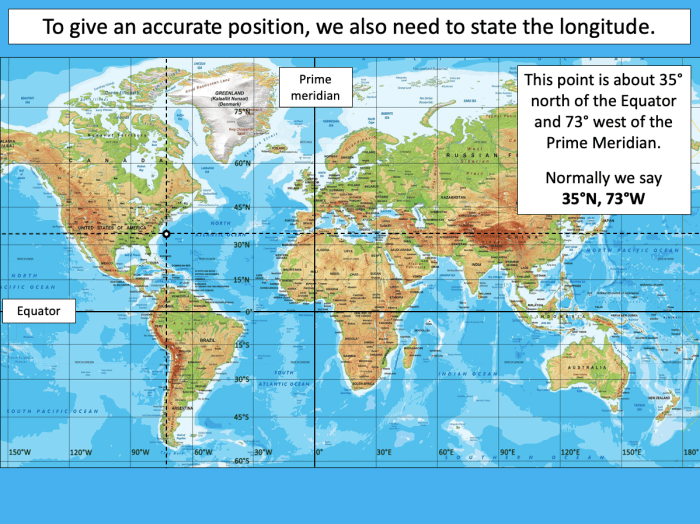
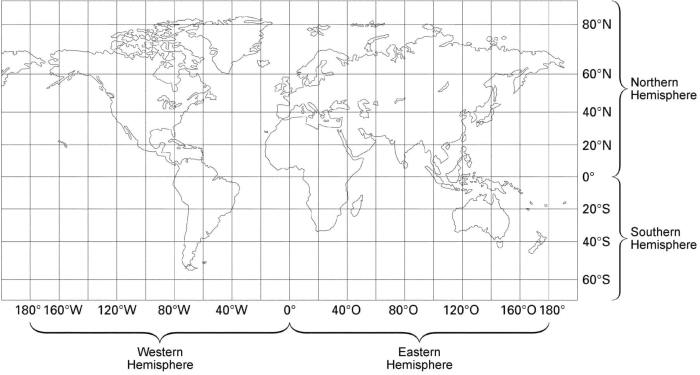
Latitude and longitude are two essential geographic coordinates used to locate any point on the Earth’s surface. Latitude measures the position north or south of the equator, while longitude measures the position east or west of the prime meridian.
Latitude and longitude are crucial for navigation, mapping, and surveying. They enable us to determine the precise location of places, measure distances, and navigate from one point to another.
Understanding Coordinates
Latitude and longitude coordinates are expressed in degrees, minutes, and seconds (DMS) or decimal degrees (DD). In DMS, each degree is divided into 60 minutes, and each minute is further divided into 60 seconds. Decimal degrees represent a continuous measure of degrees, with decimal values representing fractions of a degree.
- Degrees (°): The largest unit, ranging from 0° at the equator to 90° at the poles.
- Minutes (‘): Subdivisions of degrees, with 60 minutes in each degree.
- Seconds (“): Subdivisions of minutes, with 60 seconds in each minute.
- Decimal Degrees (DD): A continuous representation of degrees, with decimal values representing fractions of a degree.
Using Worksheets for Practice
Worksheets provide a valuable tool for practicing the use of latitude and longitude. They include exercises that involve:
- Locating points on a map using latitude and longitude coordinates.
- Converting between different coordinate formats (DMS and DD).
By completing these exercises, students can improve their understanding of latitude and longitude and develop their map-reading skills.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios, Using latitude and longitude worksheet
Latitude and longitude are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Navigation systems: GPS devices and mapping apps use latitude and longitude to determine the user’s location and provide directions.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): GIS software uses latitude and longitude to store and analyze spatial data, allowing users to create maps and conduct spatial analysis.
- Surveying and land measurement: Surveyors use latitude and longitude to accurately measure and map land boundaries and features.
Advanced Concepts
Beyond basic navigation, latitude and longitude are also used for more advanced applications:
- Calculating distances and areas on a map: Using trigonometry and the Earth’s radius, latitude and longitude can be used to calculate the distance between two points or the area of a region.
- Datums and projections: Different datums (reference points) and map projections can affect the accuracy of latitude and longitude coordinates. Understanding these concepts is essential for precise geospatial analysis.
FAQ Section
What is the primary purpose of latitude and longitude?
Latitude and longitude form a coordinate system that uniquely identifies locations on the Earth’s surface, enabling precise navigation and mapping.
How do I read latitude and longitude coordinates?
Latitude is measured in degrees north or south of the equator, while longitude is measured in degrees east or west of the prime meridian. Coordinates are typically expressed in degrees, minutes, and seconds, or in decimal degrees.
What are some real-world applications of latitude and longitude?
Latitude and longitude are essential for navigation systems (GPS, mapping apps), Geographic Information Systems (GIS), surveying, land measurement, and various scientific and engineering applications.