Types of continuous measurement aba – Continuous measurement in applied behavior analysis (ABA) is a powerful tool that allows practitioners to objectively and accurately assess and quantify behavior. By utilizing various types of continuous measurement, ABA professionals can gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of interventions and make data-driven decisions to improve outcomes for individuals with autism spectrum disorder and other developmental disabilities.
This guide will delve into the different types of continuous measurement used in ABA, exploring their advantages, disadvantages, and appropriate applications. We will also discuss the importance of data collection and analysis, as well as the practical applications of continuous measurement in ABA practice.
Continuous Measurement in ABA

Continuous measurement is a data collection method in applied behavior analysis (ABA) that involves recording the frequency, duration, or intensity of a behavior over time. It is a valuable tool for assessing the effectiveness of interventions and making data-based decisions.
Benefits of Continuous Measurement in ABA
Continuous measurement offers several benefits, including:
Provides a detailed and accurate record of behavior
Continuous measurement allows researchers and practitioners to capture the precise frequency, duration, or intensity of a behavior over time, providing a comprehensive understanding of the behavior’s patterns.
Enables objective and reliable data collection
Continuous measurement eliminates subjectivity and bias by using objective measures to quantify behavior, ensuring the reliability and validity of the data collected.
Facilitates the identification of behavior patterns
Continuous measurement allows researchers and practitioners to identify patterns in behavior, such as the time of day when a behavior occurs most frequently or the duration of a behavior under different conditions.
Supports evidence-based decision-making
The detailed data provided by continuous measurement enables researchers and practitioners to make informed decisions about interventions and adjust them as needed based on the data collected.
Examples of Continuous Measurement in ABA, Types of continuous measurement aba
Continuous measurement can be used in a variety of ABA settings to assess different behaviors. Some common examples include:
- Measuring the frequency of a child’s tantrums over time to evaluate the effectiveness of a behavior intervention plan.
- Recording the duration of a child’s attention to a task to assess their ability to focus and maintain attention.
- Quantifying the intensity of a person’s anxiety levels using a scale from 0 to 10 to monitor the progress of anxiety management therapy.
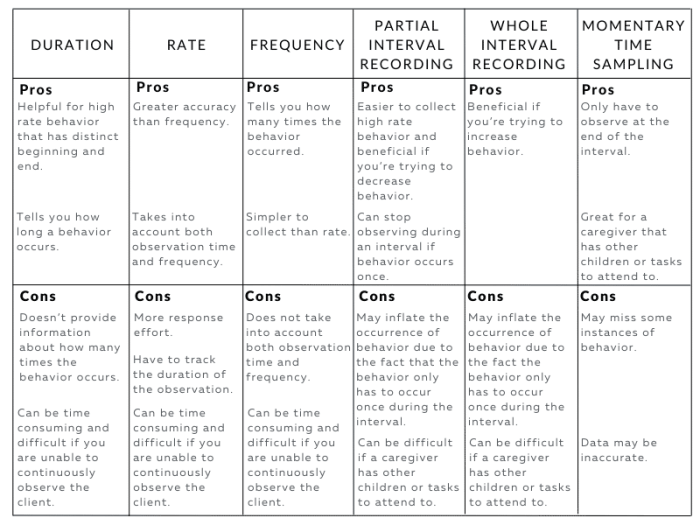
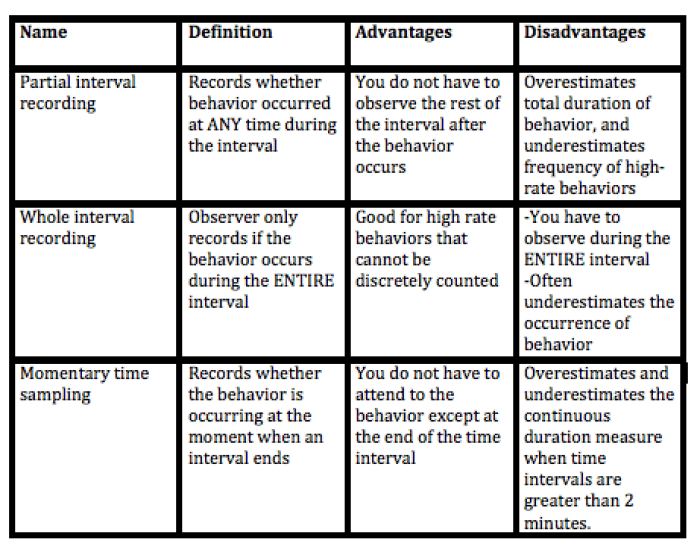
Types of Continuous Measurement
Continuous measurement in ABA involves the collection of data over time to assess an individual’s behavior. There are several types of continuous measurement used in ABA, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Interval Recording
Interval recording involves observing and recording behavior at regular intervals, such as every 5 or 10 minutes. The data is typically presented in a graph, showing the frequency or duration of the behavior over time. Interval recording is a simple and straightforward method of measurement, and it can be used to collect data on a variety of behaviors.
However, it can be difficult to accurately record behavior that occurs frequently or that is of short duration.
Event Recording
Event recording involves recording each occurrence of a behavior as it occurs. The data is typically presented in a graph, showing the number of occurrences of the behavior over time. Event recording is a more accurate method of measurement than interval recording, but it can be more time-consuming and difficult to use for behaviors that occur frequently.
Duration Recording
Duration recording involves recording the amount of time that a behavior occurs. The data is typically presented in a graph, showing the duration of the behavior over time. Duration recording is a more precise method of measurement than interval or event recording, but it can be more difficult to use for behaviors that are of short duration or that occur intermittently.
Latency Recording
Latency recording involves recording the amount of time that it takes for a behavior to occur after a specific event. The data is typically presented in a graph, showing the latency of the behavior over time. Latency recording can be used to assess the effects of interventions on the speed of responding.
Choice of Measurement Type
The choice of which type of continuous measurement to use depends on the specific behavior being assessed and the goals of the assessment. Interval recording is a good choice for behaviors that occur frequently or that are of long duration.
Event recording is a good choice for behaviors that occur infrequently or that are of short duration. Duration recording is a good choice for behaviors that are of variable duration. Latency recording is a good choice for assessing the effects of interventions on the speed of responding.
Data Collection and Analysis
In continuous measurement, data is collected over time to track changes in behavior. This data can be collected using a variety of methods, including direct observation, indirect observation, and self-report.
Once data has been collected, it is important to analyze it to identify patterns and trends. This analysis can be used to inform ABA interventions by identifying the antecedents and consequences that are maintaining the target behavior.
Reliability and Validity
Reliability and validity are two important concepts in data collection and analysis. Reliability refers to the consistency of a measurement, while validity refers to the accuracy of a measurement.
To ensure the reliability of a measurement, it is important to use a consistent method of data collection and analysis. For example, if you are using direct observation to collect data, you should use the same observation method each time you collect data.
To ensure the validity of a measurement, it is important to use a method that is appropriate for the target behavior. For example, if you are trying to measure the frequency of a behavior, you should use a method that allows you to accurately count the number of times the behavior occurs.
Using Data to Inform ABA Interventions
Data can be used to inform ABA interventions in a variety of ways. For example, data can be used to:
- Identify the antecedents and consequences that are maintaining the target behavior
- Develop and implement effective interventions to change the target behavior
- Evaluate the effectiveness of ABA interventions
By using data to inform ABA interventions, you can increase the likelihood of success.
Applications of Continuous Measurement
Continuous measurement plays a crucial role in ABA, providing valuable data for intervention design, implementation, and evaluation. It enables practitioners to track changes in behavior over time, identify patterns, and make informed decisions to optimize treatment outcomes.
Improving ABA Interventions
- Tailored Interventions:Continuous measurement allows practitioners to tailor interventions to the specific needs of each individual. By tracking progress, they can identify areas requiring additional support and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Objective Data:Continuous measurement provides objective data that can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. Practitioners can compare pre- and post-intervention data to measure progress and make necessary modifications.
- Early Detection of Changes:Continuous measurement enables early detection of changes in behavior, allowing practitioners to intervene promptly and prevent setbacks.
Areas for Advancement
- Remote Monitoring:Continuous measurement can be integrated into wearable devices or mobile apps, enabling remote monitoring of behavior. This allows practitioners to track progress outside of therapy sessions and provide timely support.
- Predictive Analytics:Continuous measurement data can be analyzed using predictive analytics to identify patterns and forecast future behavior. This information can be used to develop proactive strategies and prevent potential challenges.
- Automated Interventions:Continuous measurement can be coupled with automated interventions, such as smartphone notifications or smart home devices, to provide immediate feedback and reinforcement for desired behaviors.
FAQ Guide: Types Of Continuous Measurement Aba
What are the benefits of using continuous measurement in ABA?
Continuous measurement provides objective and quantifiable data, allowing for precise assessment of behavior and the effectiveness of interventions.
What are the different types of continuous measurement used in ABA?
Common types include interval recording, ratio recording, and duration recording, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
How is data collected and analyzed in continuous measurement?
Data is typically collected using observation and recording techniques, and analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns and trends.