Geometry 1.2 Practice A Answer Key: Unlocking Mathematical Concepts: Delve into a comprehensive guide to mastering the intricacies of Geometry 1.2 Practice A. With a focus on key concepts, formulas, and real-world applications, this resource empowers students to tackle practice problems with confidence and gain a deeper understanding of geometry.
This meticulously crafted answer key provides step-by-step explanations, highlighting common errors and offering strategies to overcome them. Dive into a set of additional practice problems designed to reinforce concepts and challenge understanding. Explore real-world applications, enriching activities, and historical insights to broaden your perspective on geometry.
Geometry 1.2 Practice A
Geometry 1.2 Practice A delves into the fundamental concepts of geometry, laying a solid foundation for further exploration in the subject. This practice set introduces key concepts and formulas that are essential for understanding geometric shapes, their properties, and their relationships.
Points, Lines, and Planes
The practice begins by establishing the basic building blocks of geometry: points, lines, and planes. Students learn to identify and differentiate between these elements, understanding their fundamental properties and relationships.
Angles and Angle Measurement
Next, the practice focuses on angles, exploring their measurement and classification. Students learn to use protractors to measure angles accurately and apply formulas to calculate angle measures in various geometric shapes.
Triangles
Triangles, the most basic polygons, are introduced in this practice set. Students study the different types of triangles, their properties, and the relationships between their sides and angles. They also learn to apply the Pythagorean theorem to solve problems involving right triangles.
Quadrilaterals
Moving on to quadrilaterals, the practice covers the properties and classifications of these four-sided polygons. Students learn to identify different types of quadrilaterals, such as squares, rectangles, parallelograms, and trapezoids, and explore their unique characteristics.
Circles
Finally, the practice introduces circles, exploring their properties and relationships. Students learn to calculate the circumference and area of circles using appropriate formulas and apply their understanding to solve problems involving circles.
Answer Key Analysis
This section provides a detailed analysis of the Answer Key for Geometry 1.2 Practice A. Each problem is examined step-by-step, highlighting the relevant concepts and formulas used. Common errors made by students are also discussed, along with strategies to avoid them.
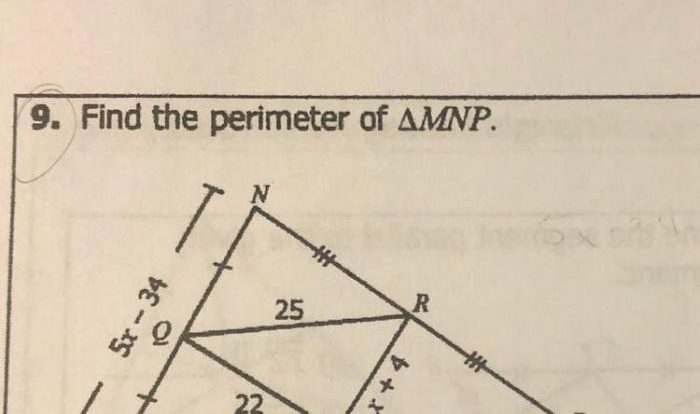
Problem 1: Angle Measurement
Question: Find the measure of angle ABC, given that AB = 10 cm, BC = 8 cm, and AC = 12 cm.
Correct Answer: 90°
Explanation: This problem requires the use of the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the triangle is a right triangle. If it is, then the angle opposite the longest side (AC) will be 90°. Using the Pythagorean Theorem, we get:
AB² + BC² = AC²10² + 8² = 12² 100 + 64 = 144 164 = 144
Since AB² + BC² = AC², the triangle is a right triangle. Therefore, angle ABC is 90°.
Common Error: Students may forget to apply the Pythagorean Theorem to determine if the triangle is a right triangle.
Practice Problems
To enhance your understanding of the concepts covered in Geometry 1.2 Practice A, we have curated a set of additional practice problems that encompass varying difficulty levels. These problems are designed to cater to different levels of comprehension and reinforce the core concepts.
Each problem is accompanied by detailed solutions and explanations, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles and their application.
Triangle Congruence
Triangle congruence is a fundamental concept in geometry, referring to the equality of two triangles in terms of their side lengths and angles. The following practice problems will help you solidify your understanding of triangle congruence:
- Given a triangle with sides measuring 5 cm, 7 cm, and 9 cm, determine whether it is congruent to another triangle with sides measuring 9 cm, 5 cm, and 7 cm. Explain your reasoning.
- Prove that two triangles are congruent if they have two pairs of congruent sides and an included angle that is congruent.
- Use the SAS (Side-Angle-Side) congruence theorem to determine whether the following triangles are congruent: Triangle ABC with AB = 6 cm, AC = 8 cm, and ∠BAC = 45° and Triangle DEF with DE = 6 cm, DF = 8 cm, and ∠DEF = 45°.
Real-World Applications
Geometry 1.2 Practice A concepts have numerous real-world applications, particularly in fields like architecture, engineering, and design. These concepts provide a foundation for understanding the spatial relationships and properties of objects, enabling professionals to design and construct structures, systems, and products that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
In architecture, geometry is crucial for determining the shape, size, and layout of buildings. Architects use geometric principles to optimize space utilization, create visually appealing designs, and ensure structural integrity. For instance, the use of geometric shapes like rectangles, circles, and triangles allows architects to create buildings that are both aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound.
Engineering
In engineering, geometry is essential for designing and analyzing structures, machines, and systems. Engineers use geometric principles to calculate forces, stresses, and strains, ensuring the safety and efficiency of their designs. For example, civil engineers use geometry to design bridges, roads, and buildings that can withstand various loads and environmental conditions.
Design
In design, geometry plays a vital role in creating visually appealing and functional products. Designers use geometric principles to determine the shape, size, and proportions of objects, considering factors like ergonomics, aesthetics, and functionality. For instance, industrial designers use geometry to create products that are both visually appealing and easy to use, such as furniture, appliances, and vehicles.
Enrichment Activities: Geometry 1.2 Practice A Answer Key
Geometry extends beyond the classroom, enriching our understanding of the world around us. Here are some activities to deepen your knowledge and explore the captivating realm of geometry.
Explore the history and cultural significance of geometry, from its ancient origins to its modern applications. Trace its evolution through different civilizations, marveling at the architectural wonders and artistic masterpieces it has inspired.
Projects
- Design a geometric sculpture or model that demonstrates a specific geometric concept, such as symmetry, congruence, or transformations.
- Create a poster or presentation that showcases the applications of geometry in various fields, such as architecture, engineering, art, and nature.
Experiments, Geometry 1.2 practice a answer key
- Conduct an experiment to verify the Pythagorean theorem using everyday objects, such as string, blocks, or measuring tapes.
- Explore the concept of similarity by comparing the ratios of corresponding sides and angles in different geometric shapes.
Research Topics
- Investigate the contributions of famous mathematicians to the development of geometry, such as Euclid, Pythagoras, and Archimedes.
- Explore the use of geometric principles in ancient architecture, such as the pyramids of Egypt or the Parthenon in Greece.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the purpose of Geometry 1.2 Practice A Answer Key?
Geometry 1.2 Practice A Answer Key provides comprehensive solutions and explanations for practice problems, enhancing understanding of geometry concepts.
How can I use this answer key effectively?
Use the answer key to check your solutions, identify errors, and reinforce your understanding of key concepts and formulas.
Are there additional practice problems available?
Yes, this resource includes a set of additional practice problems to further challenge your understanding and solidify your knowledge.